Overview Ordinate Dimensional Studies:
On the CAD/Blueprint resource page, I have compiled a list of Ordinate Dimensional studies for various aircraft. The purpose of these studies is to gather all known dimensional information in a format that can be easily transferred to any CAD system. Additionally, they serve as a dimensional check to verify the designer’s intent and assess the accuracy of data from different resources, including blueprints, manuals, and correspondence.
Let me give you an example:
I am currently updating the CAD/ordinate dataset for the Grumman Goose and have already identified a few anomalies in the empennage. This document includes the layout study for the elevator, and you will notice that, based on the blueprint dimensions, the trim tab is incorrectly positioned.

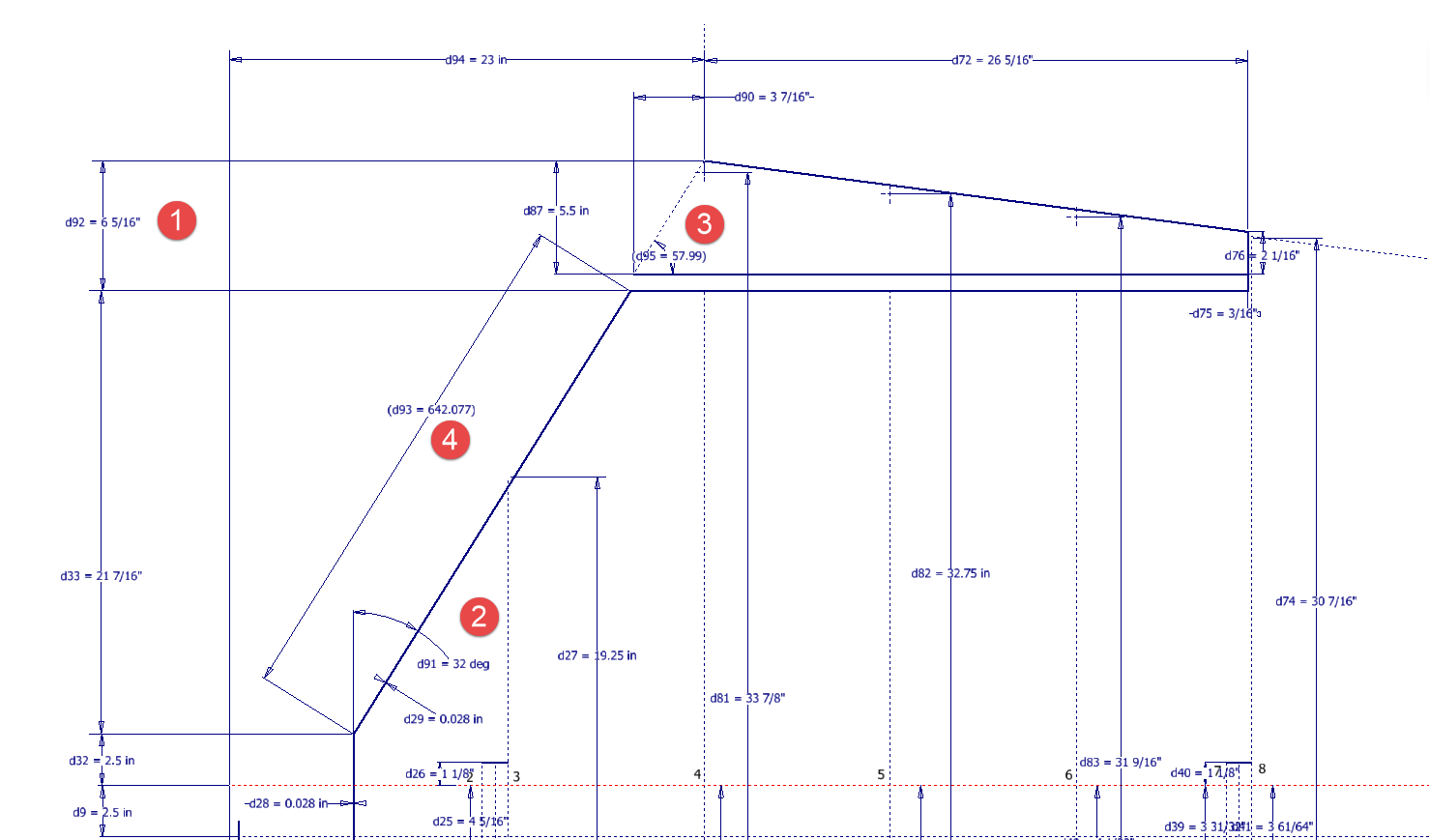
At first glance, it may seem that the dimension labeled “1” is incorrect, as it appears to be the catalyst that causes the trim tab to go out of alignment. However, when we consider the length of the diagonal line labeled “4,” which measures 642.07 mm (25.27 inches), we find a discrepancy with the blueprint that specifies this dimension as 25 inches. Additionally, this measurement does not align with the chord dimension for the rib labeled “2.” As it stands, the angle of the sloping line appears to match at 32 degrees for both the trim tab and the elevator.
This type of issue frequently arises when working from blueprints for any aircraft project. To address it, further research is required, which will involve cross-referencing all part and sub-assembly blueprints in the affected area, reviewing general arrangement layouts, and consulting relevant manuals. It is essential to understand the design intent in order to develop the most likely solution. I have even extracted key information from correspondence that was important for the P-51 Mustang.
Small dimensional discrepancies are common in these projects, not only due to converting inch dimensions to millimeters but also because of typographical errors on the blueprints themselves.


The screenshots of the Ordinate spreadsheets display the dimensional information for the Horizontal Stabilizer and the Rudder. Several dimensions are highlighted in red, indicating errors on the blueprints that have been corrected. The dimensions marked in gray represent the measured dimensions from the CAD model. This discrepancy arises from the inherent accuracy of the specified dimensions, which may only be precise to 1/32″. As a result, minor deviations can occur during the CAD development process. Understanding these differences requires careful consideration of all key layout dimensions and material thicknesses, as they all influence the final derived dimensions. Nothing is taken for granted.
The CAD/Ordinate datasets compile all known dimensional information from various thoroughly researched sources, providing a comprehensive collection of data. This data is presented in editable spreadsheets, fully dimensioned drawings, and 2D/3D CAD drawings and models.
Elevator Layout Solution:
I have identified a solution regarding the layout dimensions. The dimension labeled as “1” is incorrect, but it is not the primary issue. Firstly, the Trim Tab has its own drawing #12530, which indicates that the overall length of the tab is 28.75″. This measurement is incorrect; it should be 29.75″. Additionally, other dimensions are also contributing factors.


In the bottom left corner, we find the specifications for the Hinge and Torque Tube, where two dimensions are marked with a tilde underscore to indicate that they are approximate. Generally, approximate dimensions are expected to be close to the actual measurements; however, that is not the case here. By adjusting the overall length of the Trim Tab along with modifying the approximate dimensions at the hinge torque, and also ensuring proper alignment with the known trailing edge, I have arrived at a workable and accurate solution.

Tech Tip: Using the Ordinate Spreadsheets:
I often get asked this and I have written about using the Ordinate spreadsheets before. Bumping it up to a more recent post, this one; I thought I would share a quick tip.
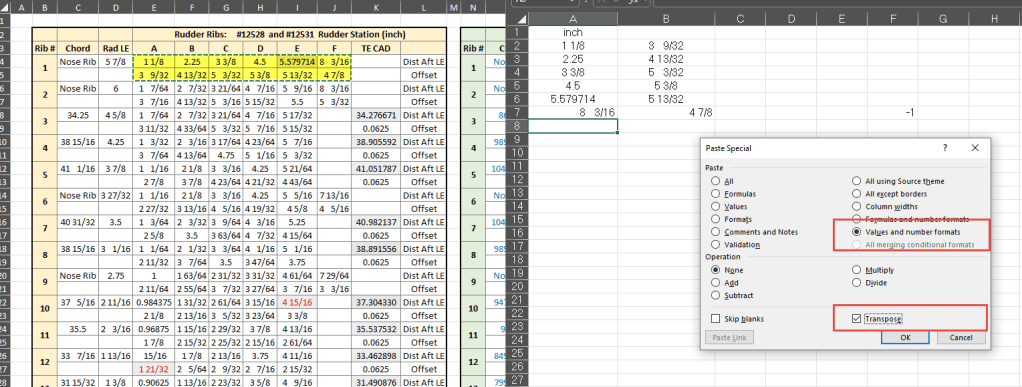
The Ordinate data spreadsheet is on the left, while the other is an empty spreadsheet that I use to paste data for a specific frame or rib that the CAD system can access. The empty spreadsheet just sits on my desktop, which makes it accessible.
Generally, the format of the data table is set out according to the original resource, which makes it easier to cross reference and check. This is not entirely ideal for CAD access as the X, Y coordinates are in rows and not in columns. The fix for that is easy, copy the data from the spreadsheet as required, select Paste Special in the destination spreadsheet making sure to select the “Values and Formats” and the “Transpose” options. The former ensures the data format remains the same and the purpose of the Transpose function is to convert data rows to columns. This gives us the data in X, Y columns ready for insert into the CAD system.
Note the “inch” header…I am using a millimetre template in my CAD system so I have to specify the unit of measure when I select from the first table. By the way, there is a second table that has all those values converted to millimeter anyway, so we could easily use that…in this case, you would not require a header row.
In other datasets, I have developed additional data tables in the spreadsheet, where I have transposed columns for the X, Y, and Z coordinates, such as those for the P-39.

I receive a lot of feedback from users about the spreadsheets, specifically regarding the time they save on projects since they do not have to manually input data themselves.